Network Engineering Basics – Part 2:
Now that you understand what a network is, the next step is learning about the devices that make networks work. Although modems, routers, and switches often look similar, they each serve a very different purpose.
In this article, we’ll clearly explain what modems, routers, and switches are, how they differ, and how they work together in real-world networks.
Why These Devices Matter
Before diving into details, it helps to understand why these devices are so important. Every home, office, and data center relies on them to move data efficiently and securely.
However, confusion is common. Many people assume one device does everything. In reality, each device has a specific role.
What Is a Modem?
A modem connects your local network to your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
In simple terms, the modem:
- Brings the internet into your home or office
- Converts ISP signals into usable network data
- Acts as the gateway to the public internet
Without a modem, your network would not be able to access the internet at all.
Important Thing to Remember
A modem does not manage traffic inside your network. Instead, it only handles communication with your ISP.
What Is a Router?
A router connects multiple devices together and directs traffic between them.
More importantly, a router:
- Assigns IP addresses to devices (DHCP)
- Decides where data should go
- Connects your network to the internet
- Provides basic security features like firewalls and NAT
- Often includes Wi-Fi functionality
Because of this, the router acts as the brain of the network.
What Is a Switch?
A switch connects multiple devices within the same local network and allows them to communicate efficiently.
Unlike a router, a switch:
- Does not connect directly to the internet
- Does not assign IP addresses
- Focuses on fast, local data delivery
Switches are commonly used when:
- You need more wired ports
- Multiple computers or servers must communicate
- Performance and reliability matter
How These Devices Work Together
In most networks, these devices form a simple chain.
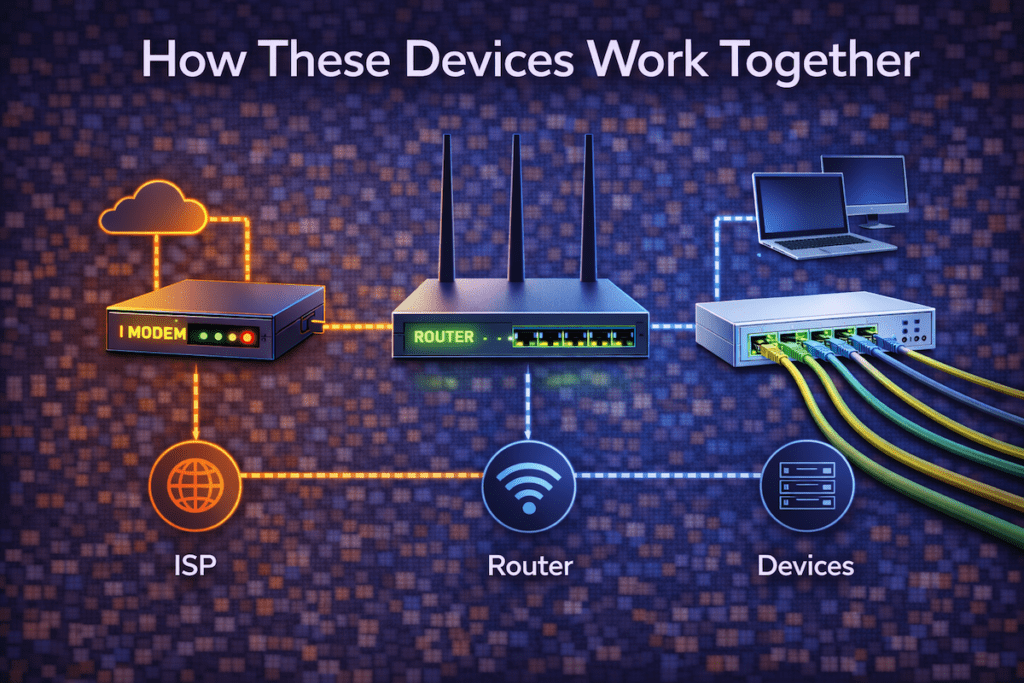
Here’s a typical setup:
- The modem connects to the ISP
- The router connects to the modem
- The switch connects to the router
- Devices connect to the router or switch
As a result, data can flow smoothly from local devices to the internet and back.
Simple Comparison: Modem vs Router vs Switch
| Device | Primary Role | Internet Connection | Manages Local Traffic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modem | Connects to ISP | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Router | Directs traffic | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Switch | Connects devices | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
This table highlights why each device exists and why none of them fully replace the others.
All-in-One Modem and Router Devices
Many ISPs provide modem-router combo units. While these devices are convenient, they come with trade-offs.
Advantages
- Easy to set up
- Fewer cables and devices
- Lower upfront cost
Disadvantages
- Limited customization
- Harder to upgrade
- Less control for advanced users
For beginners, combos work well. However, engineers often prefer separate devices for flexibility.
Home Networks vs Business Networks
Home Networks
Most homes use:
- One modem
- One router (often with built-in Wi-Fi)
- Optional small switch
This setup is simple and effective for everyday use.
Business Networks
Businesses often require:
- Dedicated firewalls
- High-performance routers
- Managed switches
- Network segmentation
As networks grow, separation of roles becomes increasingly important.
Common Beginner Mistakes
Beginners often:
- Expect a switch to provide internet access
- Think Wi-Fi replaces a router
- Plug devices into a modem directly
Understanding each device’s role helps prevent these issues early on.
Why Network Engineers Must Understand These Basics
Network engineering builds on these core concepts. Without understanding what modems, routers, and switches do, advanced topics like VLANs, routing protocols, and security become much harder.
Therefore, mastering these fundamentals is essential before moving forward.
What’s Next in the Series
Now that you understand the core network devices, the next step is learning how devices identify each other.
This upcoming article will explain how devices find each other on a network and why IP addressing matters.
Final Thoughts
Although modems, routers, and switches are often grouped together, they serve very different roles. Once you understand how they work individually and together, networking becomes much easier to grasp.
This knowledge forms a critical foundation for everything that follows in network engineering.
Welcome back to Network Engineering Basics on Relay Rack 1.


Thanks, this clear up some confusion I had. I thought they were all one device.